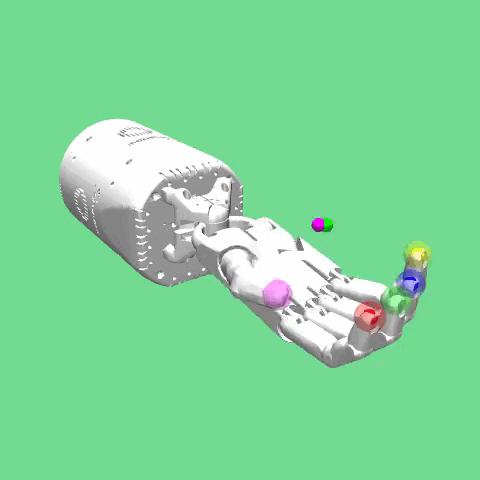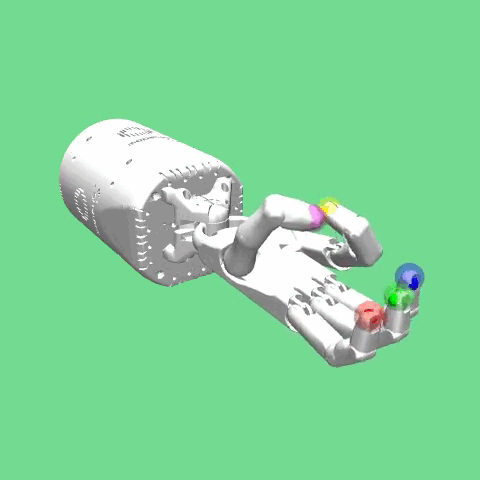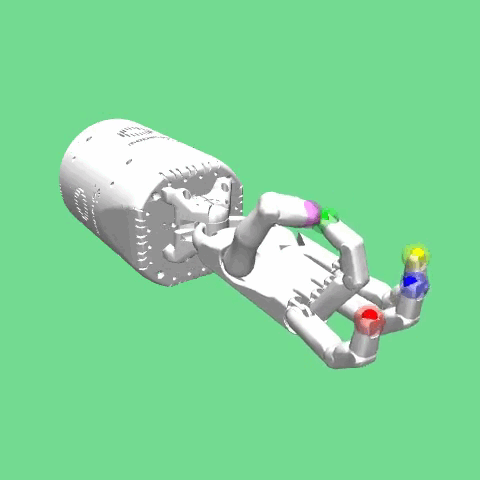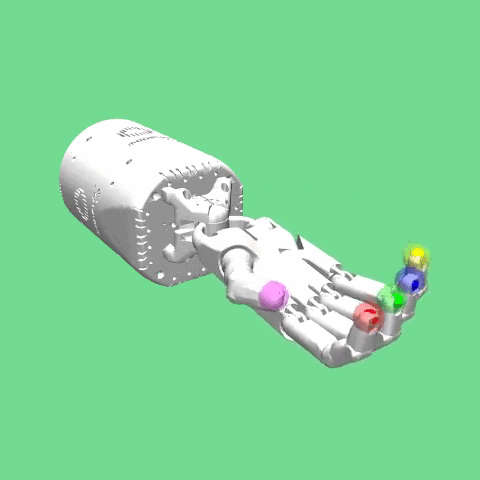
Reach¶
Description¶
This environment was introduced in “Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning: Challenging Robotics Environments and Request for Research”.
The environment is based on the Shadow Dexterous Hand, which is an antropomorphic robotic hand with 24 joints. The goal of the task is for the fingertips of the hand to reach a predefined target Cartesian position.
The hand has a total of 20 motor controlled degrees of freedom out of the 24 joints. The thumb has 5 joints and 5 DoF while the rest of the fingers have 4 joints and 3 DoF (each finger’s distal joint is coupled with a tendon to its middle joint
just like a human hand, so that the middle joint angle is always greater or equal to the distal joint angle). The control frequency of the actuators is of f = 25 Hz. This is achieved by applying the same action in 20 subsequent simulator step
(with a time step of dt = 0.002 s) before returning the control to the robot.
The kinematics of the Shadow Dexterous Hand resembles that of the human hand. The robot hand has 2 degrees of freedom for the wrist to perform the radial/lunar deviation movements (WRJ1) and flexion/extension (WRJ0). Each finger has three joints
in common. The joint closer to the palm is called metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and has a total of 2 degrees of freedom each. In the robot they are defined as FFJ3, MFJ3, RFJ3, LFJ3, and THJ2 (forefinger, middle finger, ring finger, little
finger, and thumb respectively) for the adduction/abduction degree of freedom, and FFJ2, MFJ2, RFJ2, LFJ2, THJ1 for the flexion/extension DoF. The middle joint in the fingers is known as proximal interphalangea (PIP), which in the robot hand
correspond to FFJ1, MFJ1, RFJ1, and LFJ1. This joint is also responsible for flexion/extension. The last joint in common is the most distant to the palm, called distal interphalangeal (DIP) and in the robot hand FFJ0, MFJ0, RFJ0, and LFJ0.
This joint is not actuated but coupled to the PIP joints by tendons in MuJoCo.
In the robot hand an extra joint is added to the little finger LFJ4 in order to perform the opposition movement with the thumb. Also the the human thumb has two different joints than the rest of the fingers. The carpometacarpal (CMC) joint located close
to the palm area, THJ4 and THJ3in the robot. And the interphalangeal joint which is in the same location as the DIP but in this case actuated. This joint is the THJ0 in the robot hand.
Action Space¶
The action space is a Box(-1.0, 1.0, (20,), float32). The control actions are absolute angular positions of the actuated joints (non-coupled). The input of the control actions is set to a range between -1 and 1 by scaling the actual actuator angle ranges.
The elements of the action array are the following:
Num |
Action |
Control Min |
Control Max |
Angle Min |
Angle Max |
Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint (radial/ulnar deviation) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.489 (rad) |
0.14 (rad) |
robot0:A_WRJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.698 (rad) |
0.489 (rad) |
robot0:A_WRJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_FFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_FFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the forefinger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_FFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_MFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_MFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the middle finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_MFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
8 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_RFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
9 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_RFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
10 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_RFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
11 |
Angular position of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
0.785(rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the little finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
15 |
Horizontal angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-1 |
1 |
-1.047 (rad) |
1.047 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
16 |
Vertical Angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.222 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
17 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.209 (rad) |
0.209(rad) |
robot0:A_THJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
18 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.524 (rad) |
0.524 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
19 |
Angular position of the IP joint of the thumb finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-1.571 (rad) |
0 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
Observation Space¶
The observation is a goal-aware observation space. It consists of a dictionary with information about the robot’s joint and finger states, as well as information about the goal. The finger tip observations are derived from
Mujoco bodies known as sites attached to the body of interest such as the finger tips. The dictionary consists of the following 3 keys:
observation: its value is anndarrayof shape(63,). It consists of kinematic information of the block object and gripper. The elements of the array correspond to the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Angular position of the vertical wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinge |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
8 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
9 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
10 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
11 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Angular position of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ4 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
15 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
16 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
17 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
18 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
19 |
Horizontal angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ4 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
20 |
Vertical Angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
21 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
22 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
23 |
Angular position of the IP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
24 |
Angular velocity of the horizontal wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
25 |
Angular velocity of the vertical wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
26 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
27 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the forefinge |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
28 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
29 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
30 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
31 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
32 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
33 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
34 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
35 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
36 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
37 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
38 |
Angular velocity of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ4 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
39 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
40 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
41 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
42 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
43 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ4 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
44 |
Vertical Angular velocity of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
45 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
46 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
47 |
Angular velocity of the IP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
48 |
x coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_fftip |
- |
position (m) |
49 |
y coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_fftip |
- |
position (m) |
50 |
z coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_fftip |
- |
position (m) |
51 |
x coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_mftip |
- |
position (m) |
52 |
y coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_mftip |
- |
position (m) |
53 |
z coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_mftip |
- |
position (m) |
54 |
x coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_rftip |
- |
position (m) |
55 |
y coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_rftip |
- |
position (m) |
56 |
z coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_rftip |
- |
position (m) |
57 |
x coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_lftip |
- |
position (m) |
58 |
y coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_lftip |
- |
position (m) |
59 |
z coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_lftip |
- |
position (m) |
60 |
x coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_thtip |
- |
position (m) |
61 |
y coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_thtip |
- |
position (m) |
62 |
z coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:S_thtip |
- |
position (m) |
desired_goal: this key represents the final goal to be achieved. In this environment it is a 15-dimensionalndarray,(15,), that consists of the 15 cartesian coordinates of the desired final finger tip position[x,y,z]. The elements of the array are the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Target x coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target0 |
position (m) |
1 |
Target y coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target0 |
position (m) |
2 |
Target z coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target0 |
position (m) |
3 |
Target x coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target1 |
position (m) |
4 |
Target y coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target1 |
position (m) |
5 |
Target z coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target1 |
position (m) |
6 |
Target x coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target2 |
position (m) |
7 |
Target y coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target2 |
position (m) |
8 |
Target z coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target2 |
position (m) |
9 |
Target x coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target3 |
position (m) |
10 |
Target y coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target3 |
position (m) |
11 |
Target z coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target3 |
position (m) |
12 |
Target x coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target4 |
position (m) |
13 |
Target y coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target4 |
position (m) |
14 |
Target z coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
target4 |
position (m) |
achieved_goal: this key represents the current state of the fingers, as if it would have achieved a goal. This is useful for goal orientated learning algorithms such as those that use Hindsight Experience Replay (HER). The value is anndarraywith shape(15,). The elements of the array are the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Current x coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_fftip |
position (m) |
1 |
Current y coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_fftip |
position (m) |
2 |
Current z coordinate of the tip of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_fftip |
position (m) |
3 |
Current x coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_mftip |
position (m) |
4 |
Current y coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_mftip |
position (m) |
5 |
Current z coordinate of the tip of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_mftip |
position (m) |
6 |
Current x coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_rftip |
position (m) |
7 |
Current y coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_rftip |
position (m) |
8 |
Current z coordinate of the tip of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_rftip |
position (m) |
9 |
Current x coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_lftip |
position (m) |
10 |
Current y coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_lftip |
position (m) |
11 |
Current z coordinate of the tip of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_lftip |
position (m) |
12 |
Current x coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_thtip |
position (m) |
13 |
Current y coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_thtip |
position (m) |
14 |
Current z coordinate of the tip of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:S_thtip |
position (m) |
Rewards¶
The reward can be initialized as sparse or dense:
sparse: the returned reward can have two values:
-1if the fingers haven’t reached their final target position, and0if the fingers are in their final target position (the fingers are considered to have reached their goal if the 2-nom between the achieved goal vector and the desired goal vector is lower than 0.01).dense: the returned reward is the negative 2-norm distance between the achieved goal vector and the desired goal vector.
To initialize this environment with one of the mentioned reward functions the type of reward must be specified in the id string when the environment is initialized. For sparse reward the id is the default of the environment, HandReach-v2.
However, for dense reward the id must be modified to HandReachDense-v2 and initialized as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
env = gym.make('HandReachDense-v2')
Starting State¶
When the environment is reset the joints of the hand are initialized with the following angles (rad):
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Angle (rad) |
|---|---|
robot0:WRJ1 |
-0.16514339750464327 |
robot0:WRJ0 |
-0.31973286565062153 |
robot0:FFJ3 |
0.14340512546557435 |
robot0:FFJ2 |
0.32028208333591573 |
robot0:FFJ1 |
0.7126053607727917 |
robot0:FFJ0 |
0.6705281001412586 |
robot0:MFJ3 |
0.000246444303701037 |
robot0:MFJ2 |
0.3152655251085491 |
robot0:MFJ1 |
0.7659800313729842 |
robot0:MFJ0 |
0.7323156897425923 |
robot0:RFJ3 |
0.00038520700007378114 |
robot0:RFJ2 |
0.36743546201985233 |
robot0:RFJ1 |
0.7119514095008576 |
robot0:RFJ0 |
0.6699446327514138 |
robot0:LFJ4 |
0.0525442258033891 |
robot0:LFJ3 |
-0.13615534724474673 |
robot0:LFJ2 |
0.39872030433433003 |
robot0:LFJ1 |
0.7415570009679252 |
robot0:LFJ0 |
0.704096378652974 |
robot0:THJ4 |
0.003673823825070126 |
robot0:THJ3 |
0.5506291436028695 |
robot0:THJ2 |
-0.014515151997119306 |
robot0:THJ1 |
-0.0015229223564485414 |
robot0:THJ0 |
-0.7894883021600622 |
For the target cartersian position of the fingers there are two possible initializations chosen randomly. With a probability of 10 % the episodes goal will be to keep the initial position of the finger tips for an indefinite period of time. The initial position of the finger tips will then be:
Finger Tip |
Coordinate |
Position (m) |
|---|---|---|
Forefinger |
x |
0.99 |
Forefinger |
y |
0.8 |
Forefinger |
z |
0.15 |
Middle |
x |
1.02 |
Middle |
y |
0.8 |
Middle |
z |
0.15 |
Ring |
x |
1.04 |
Ring |
y |
0.81 |
Ring |
z |
0.155 |
Little |
x |
1.07 |
Little |
y |
0.82 |
Little |
z |
0.16 |
Thumb |
x |
0.95 |
Thumb |
y |
0.84 |
Thumb |
z |
0.16 |
In the other possible episode intializaitons one of the fingers is randomly selected to meet the tip of the thumb over the palm of the hand. The rest of the finger tips must maintain the initial positions mentioned before.
Episode End¶
The episode will be truncated when the duration reaches a total of max_episode_steps which by default is set to 50 timesteps.
The episode is never terminated since the task is continuing with infinite horizon.
Arguments¶
To increase/decrease the maximum number of timesteps before the episode is truncated the max_episode_steps argument can be set at initialization. The default value is 50. For example,
to increase the total number of timesteps to 100 make the environment as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
env = gym.make('HandReach-v2', max_episode_steps=100)
Version History¶
v3: Fixed bug where initial state did not match initial state description in documentation. Hand Reach environments’ initial states after reset now match the documentation (related GitHub issue).
v2: Fixed bug:
env.reset()not properly resetting the internal state. Fetch environments now properly reset their state (related GitHub issue).v1: the environment depends on the newest mujoco python bindings maintained by the MuJoCo team in Deepmind.
v0: the environment depends on
mujoco_pywhich is no longer maintained.