Manipulate Block¶
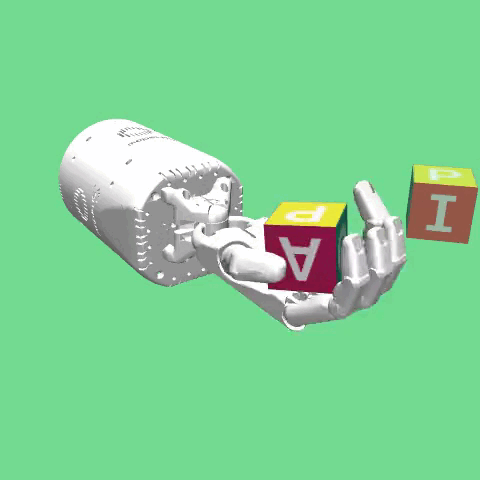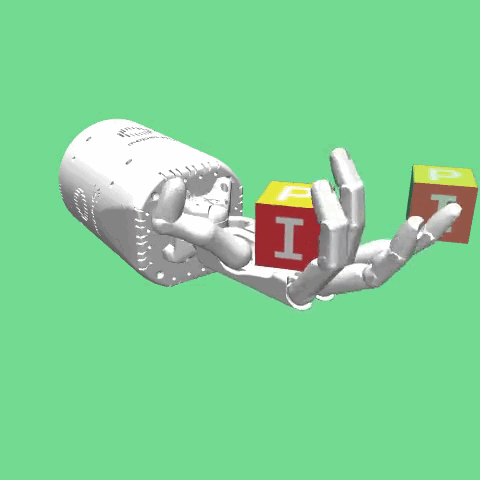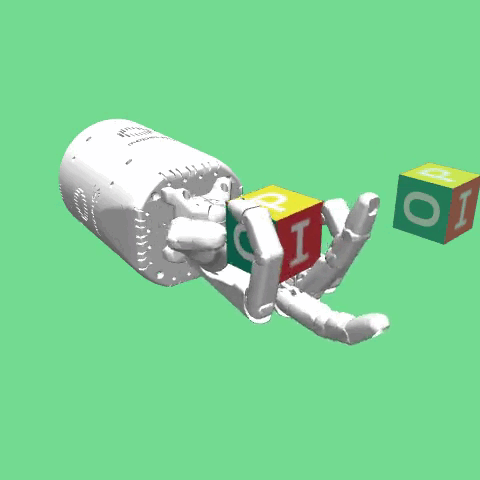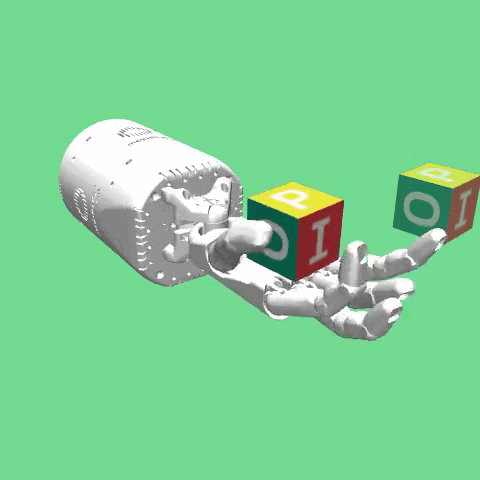
Description¶
This environment was introduced in “Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning: Challenging Robotics Environments and Request for Research”.
The environment is based on the same robot hand as in the HandReach environment, the Shadow Dexterous Hand. In this task a block is placed on the palm of the hand. The task is to then manipulate the
block such that a target pose is achieved. The goal is 7-dimensional and includes the target position (in Cartesian coordinates) and target rotation (in quaternions). In addition, variations of this environment can be used with increasing
levels of difficulty:
HandManipulateBlockRotateZ-v1: Random target rotation around the z axis of the block. No target position.HandManipulateBlockRotateParallel-v1: Random target rotation around the z axis of the block and axis-aligned target rotations for the x and y axes. No target position.HandManipulateBlockRotateXYZ-v1: Random target rotation for all axes of the block. No target position.HandManipulateBlockFull-v1: Random target rotation for all axes of the block. Random target position.
Action Space¶
The action space is a Box(-1.0, 1.0, (20,), float32). The control actions are absolute angular positions of the actuated joints (non-coupled). The input of the control actions is set to a range between -1 and 1 by scaling the actual actuator angle ranges.
The elements of the action array are the following:
Num |
Action |
Control Min |
Control Max |
Angle Min |
Angle Max |
Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint (radial/ulnar deviation) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.489 (rad) |
0.14 (rad) |
robot0:A_WRJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.698 (rad) |
0.489 (rad) |
robot0:A_WRJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_FFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_FFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the forefinger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_FFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_MFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_MFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the middle finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_MFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
8 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_RFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
9 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_RFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
10 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_RFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
11 |
Angular position of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
0.785(rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.349 (rad) |
0.349(rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the little finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.571 (rad) |
robot0:A_LFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
15 |
Horizontal angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-1 |
1 |
-1.047 (rad) |
1.047 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
16 |
Vertical Angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.222 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
17 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.209 (rad) |
0.209(rad) |
robot0:A_THJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
18 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.524 (rad) |
0.524 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
19 |
Angular position of the IP joint of the thumb finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-1.571 (rad) |
0 (rad) |
robot0:A_THJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
Observation Space¶
The observation is a goal-aware observation space. It consists of a dictionary with information about the robot’s joint and block states, as well as information about the goal. The dictionary consists of the following 3 keys:
observation: its value is anndarrayof shape(61,). It consists of kinematic information of the block object and finger joints. The elements of the array correspond to the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Angular position of the vertical wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinge |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
8 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
9 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
10 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
11 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Angular position of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
15 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
16 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
17 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
18 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
19 |
Horizontal angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
20 |
Vertical Angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
21 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
22 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
23 |
Angular position of the IP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
24 |
Angular velocity of the horizontal wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ1 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
25 |
Angular velocity of the vertical wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:WRJ0 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
26 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ3 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
27 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the forefinge |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ2 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
28 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ1 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
29 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:FFJ0 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
30 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ3 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
31 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ2 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
32 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ1 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
33 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:MFJ0 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
34 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ3 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
35 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ2 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
36 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ1 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
37 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:RFJ0 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
38 |
Angular velocity of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ4 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
39 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ3 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
40 |
Vertical angular velocity of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ2 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
41 |
Angular velocity of the PIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ1 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
42 |
Angular velocity of the DIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:LFJ0 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
43 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ4 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
44 |
Vertical Angular velocity of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ3 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
45 |
Horizontal angular velocity of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ2 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
46 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ1 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
47 |
Angular velocity of the IP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:THJ0 |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
48 |
Linear velocity of the block in x direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
velocity (m/s) |
49 |
Linear velocity of the block in y direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
velocity (m/s) |
50 |
Linear velocity of the block in z direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
velocity (m/s) |
51 |
Angular velocity of the block in x axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
52 |
Angular velocity of the block in y axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
53 |
Angular velocity of the block in z axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
54 |
Position of the block in the x coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
position (m) |
55 |
Position of the block in the y coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
position (m) |
56 |
Position of the block in the z coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
position (m) |
57 |
w component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
58 |
x component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
59 |
y component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
60 |
z component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
desired_goal: this key represents the final goal to be achieved. In this environment it is a 7-dimensionalndarray,(7,), that consists of the pose information of the block. The elements of the array are the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Target x coordinate of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
position (m) |
1 |
Target y coordinate of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
position (m) |
2 |
Target z coordinate of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
position (m) |
3 |
Target w component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
- |
4 |
Target x component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
- |
5 |
Target y component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
- |
6 |
Target z component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
target:joint |
free |
- |
achieved_goal: this key represents the current state of the block, as if it would have achieved a goal. This is useful for goal orientated learning algorithms such as those that use Hindsight Experience Replay (HER). The value is anndarraywith shape(7,). The elements of the array are the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Current x coordinate of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
position (m) |
1 |
Current y coordinate of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
position (m) |
2 |
Current z coordinate of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
position (m) |
3 |
Current w component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
4 |
Current x component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
5 |
Current y component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
6 |
Current z component of the quaternion orientation of the block |
-Inf |
Inf |
object:joint |
free |
- |
Rewards¶
The reward can be initialized as sparse or dense:
sparse: the returned reward can have two values:
-1if the block hasn’t reached its final target pose, and0if the block is in its final target pose. The block is considered to have reached its final goal if the theta angle difference (theta angle of the 3D axis angle representation is less than 0.1 and if the Euclidean distance to the target position is also less than 0.01 m.dense: the returned reward is the negative summation of the Euclidean distance to the block’s target and the theta angle difference to the target orientation. The positional distance is multiplied by a factor of 10 to avoid being dominated by the rotational difference.
To initialize this environment with one of the mentioned reward functions the type of reward must be specified in the id string when the environment is initialized. For sparse reward the id is the default of the environment, HandManipulateBlock-v1. However, for dense
reward the id must be modified to HandManipulateBlockDense-v1 and initialized as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
import gymnasium_robotics
gym.register_envs(gymnasium_robotics)
env = gym.make('HandManipulateBlock-v1')
The rest of the id’s of the other environment variations follow the same convention to select between a sparse or dense reward function.
Starting State¶
When the environment is reset the joints of the hand are initialized to their resting position with a 0 displacement. The blocks position and orientation are randomly selected. The initial position is set to (x,y,z)=(1, 0.87, 0.2) and an offset is added to each coordinate
sampled from a normal distribution with 0 mean and 0.005 standard deviation.
While the initial orientation is set to (w,x,y,z)=(1,0,0,0) and an axis is randomly selected depending on the environment variation to add an angle offset sampled from a uniform distribution with range [-pi, pi].
The target pose of the block is obtained by adding a random offset to the initial block pose. For the position the offset is sampled from a uniform distribution with range [(x_min, x_max), (y_min,y_max), (z_min, z_max)] = [(-0.04, 0.04), (-0.06, 0.02), (0.0, 0.06)]. The orientation
offset is sampled from a uniform distribution with range [-pi,pi] and added to one of the Euler axis depending on the environment variation.
Episode End¶
The episode will be truncated when the duration reaches a total of max_episode_steps which by default is set to 50 timesteps.
The episode is never terminated since the task is continuing with infinite horizon.
Arguments¶
To increase/decrease the maximum number of timesteps before the episode is truncated the max_episode_steps argument can be set at initialization. The default value is 50. For example, to increase the total number of timesteps to 100 make the environment as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
import gymnasium_robotics
gym.register_envs(gymnasium_robotics)
env = gym.make('HandManipulateBlock-v1', max_episode_steps=100)
The same applies for the other environment variations.
Version History¶
v1: the environment depends on the newest mujoco python bindings maintained by the MuJoCo team in Deepmind.
v0: the environment depends on
mujoco_pywhich is no longer maintained.