Pick And Place¶
Description¶
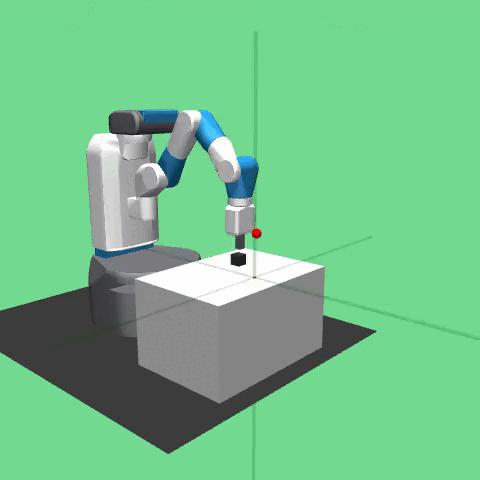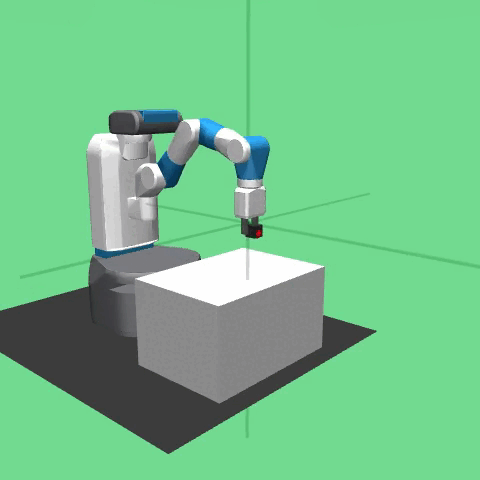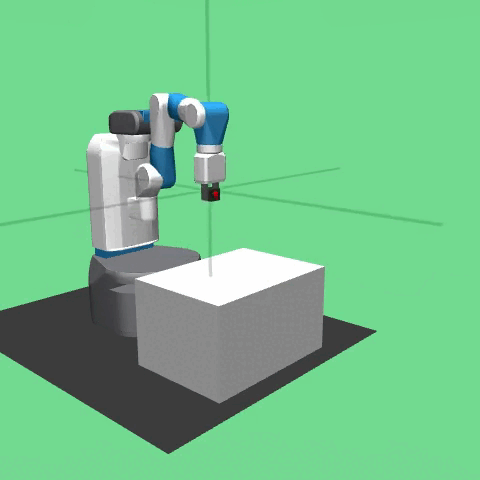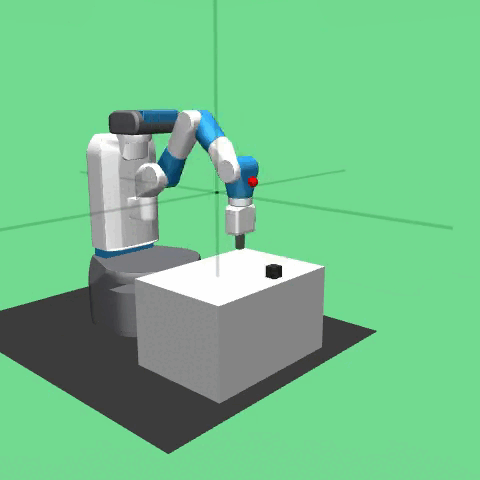
This environment was introduced in “Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning: Challenging Robotics Environments and Request for Research”.
The task in the environment is for a manipulator to move a block to a target position on top of a table or in mid-air. The robot is a 7-DoF Fetch Mobile Manipulator with a two-fingered parallel gripper. The robot is controlled by small displacements of the gripper in Cartesian coordinates and the inverse kinematics are computed internally by the MuJoCo framework. The gripper can be opened or closed in order to perform the graspping operation of pick and place. The task is also continuing which means that the robot has to maintain the block in the target position for an indefinite period of time.
The control frequency of the robot is of f = 25 Hz. This is achieved by applying the same action in 20 subsequent simulator step (with a time step of dt = 0.002 s) before returning the control to the robot.
Action Space¶
The action space is a Box(-1.0, 1.0, (4,), float32). An action represents the Cartesian displacement dx, dy, and dz of the end effector. In addition to a last action that controls closing and opening of the gripper.
Num |
Action |
Control Min |
Control Max |
Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Displacement of the end effector in the x direction dx |
-1 |
1 |
robot0:mocap |
hinge |
position (m) |
1 |
Displacement of the end effector in the y direction dy |
-1 |
1 |
robot0:mocap |
hinge |
position (m) |
2 |
Displacement of the end effector in the z direction dz |
-1 |
1 |
robot0:mocap |
hinge |
position (m) |
3 |
Positional displacement per timestep of each finger of the gripper |
-1 |
1 |
robot0:r_gripper_finger_joint and robot0:l_gripper_finger_joint |
hinge |
position (m) |
Observation Space¶
The observation is a goal-aware observation space. It consists of a dictionary with information about the robot’s end effector state and goal. The kinematics observations are derived from Mujoco bodies known as sites attached to the body of interest such as the block or the end effector.
Only the observations from the gripper fingers are derived from joints. Also to take into account the temporal influence of the step time, velocity values are multiplied by the step time dt=number_of_sub_steps*sub_step_time. The dictionary consists of the following 3 keys:
observation: its value is anndarrayof shape(25,). It consists of kinematic information of the block object and gripper. The elements of the array correspond to the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
End effector x position in global coordinates |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:grip |
- |
- |
position (m) |
1 |
End effector y position in global coordinates |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:grip |
- |
- |
position (m) |
2 |
End effector z position in global coordinates |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:grip |
- |
- |
position (m) |
3 |
Block x position in global coordinates |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
position (m) |
4 |
Block y position in global coordinates |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
position (m) |
5 |
Block z position in global coordinates |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
position (m) |
6 |
Relative block x position with respect to gripper x position in global coordinates. Equals to xblock - xgripper |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
position (m) |
7 |
Relative block y position with respect to gripper y position in global coordinates. Equals to yblock - ygripper |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
position (m) |
8 |
Relative block z position with respect to gripper z position in global coordinates. Equals to zblock - zgripper |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
position (m) |
9 |
Joint displacement of the right gripper finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:r_gripper_finger_joint |
hinge |
position (m) |
10 |
Joint displacement of the left gripper finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:l_gripper_finger_joint |
hinge |
position (m) |
11 |
Global x rotation of the block in a XYZ Euler frame rotation |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Global y rotation of the block in a XYZ Euler frame rotation |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Global z rotation of the block in a XYZ Euler frame rotation |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Relative block linear velocity in x direction with respect to the gripper |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
velocity (m/s) |
15 |
Relative block linear velocity in y direction with respect to the gripper |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
velocity (m/s) |
16 |
Relative block linear velocity in z direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
velocity (m/s) |
17 |
Block angular velocity along the x axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
18 |
Block angular velocity along the y axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
19 |
Block angular velocity along the z axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
- |
- |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
20 |
End effector linear velocity x direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:grip |
- |
- |
velocity (m/s) |
21 |
End effector linear velocity y direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:grip |
- |
- |
velocity (m/s) |
22 |
End effector linear velocity z direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
robot0:grip |
- |
- |
velocity (m/s) |
23 |
Right gripper finger linear velocity |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:r_gripper_finger_joint |
hinge |
velocity (m/s) |
24 |
Left gripper finger linear velocity |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
robot0:l_gripper_finger_joint |
hinge |
velocity (m/s) |
desired_goal: this key represents the final goal to be achieved. In this environment it is a 3-dimensionalndarray,(3,), that consists of the three cartesian coordinates of the desired final block position[x,y,z]. In order for the robot to perform a pick and place trajectory, the goal position can be elevated over the table or on top of the table. The elements of the array are the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Final goal block position in the x coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
target0 |
position (m) |
1 |
Final goal block position in the y coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
target0 |
position (m) |
2 |
Final goal block position in the z coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
target0 |
position (m) |
achieved_goal: this key represents the current state of the block, as if it would have achieved a goal. This is useful for goal orientated learning algorithms such as those that use Hindsight Experience Replay (HER). The value is anndarraywith shape(3,). The elements of the array are the following:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Current block position in the x coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
position (m) |
1 |
Current block position in the y coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
position (m) |
2 |
Current block position in the z coordinate |
-Inf |
Inf |
object0 |
position (m) |
Rewards¶
The reward can be initialized as sparse or dense:
sparse: the returned reward can have two values:
-1if the block hasn’t reached its final target position, and0if the block is in the final target position (the block is considered to have reached the goal if the Euclidean distance between both is lower than 0.05 m).dense: the returned reward is the negative Euclidean distance between the achieved goal position and the desired goal.
To initialize this environment with one of the mentioned reward functions the type of reward must be specified in the id string when the environment is initialized. For sparse reward the id is the default of the environment, FetchPickAndPlace-v3. However, for dense reward the id must be modified to FetchPickAndPlaceDense-v3 and initialized as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
import gymnasium_robotics
gym.register_envs(gymnasium_robotics)
env = gym.make('FetchPickAndPlaceDense-v3')
Starting State¶
When the environment is reset the gripper is placed in the following global cartesian coordinates (x,y,z) = [1.3419 0.7491 0.555] m, and its orientation in quaternions is (w,x,y,z) = [1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0]. The joint positions are computed by inverse kinematics internally by MuJoCo. The base of the robot will always be fixed at (x,y,z) = [0.405, 0.48, 0] in global coordinates.
The block’s position has a fixed height of (z) = [0.42] m (on top of the table). The initial (x,y) position of the block is the gripper’s x and y coordinates plus an offset sampled from a uniform distribution with a range of [-0.15, 0.15] m. Offset samples are generated until the 2-dimensional Euclidean distance from the gripper to the block is greater than 0.1 m.
The initial orientation of the block is the same as for the gripper, (w,x,y,z) = [1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0].
Finally the target position where the robot has to move the block is generated. The target can be in mid-air or over the table. The random target is also generated by adding an offset to the initial grippers position (x,y) sampled from a uniform distribution with a range of [-0.15, 0.15] m.
The height of the target is initialized at (z) = [0.42] m and an offset is added to it sampled from another uniform distribution with a range of [0, 0.45] m.
Episode End¶
The episode will be truncated when the duration reaches a total of max_episode_steps which by default is set to 50 timesteps.
The episode is never terminated since the task is continuing with infinite horizon.
Arguments¶
To increase/decrease the maximum number of timesteps before the episode is truncated the max_episode_steps argument can be set at initialization. The default value is 50. For example, to increase the total number of timesteps to 100 make the environment as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
import gymnasium_robotics
gym.register_envs(gymnasium_robotics)
env = gym.make('FetchPickAndPlace-v3', max_episode_steps=100)
Version History¶
v4: Fixed bug where initial state did not match initial state description in documentation. Fetch environments’ initial states after reset now match the documentation (related GitHub issue).
v3: Fixed bug:
env.reset()not properly resetting the internal state. Fetch environments now properly reset their state (related GitHub issue).v2: the environment depends on the newest mujoco python bindings maintained by the MuJoCo team in Deepmind.
v1: the environment depends on
mujoco_pywhich is no longer maintained.