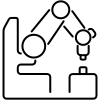
Adroit Hammer¶

Description¶
This environment was introduced in “Learning Complex Dexterous Manipulation with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Demonstrations” by Aravind Rajeswaran, Vikash Kumar, Abhishek Gupta, Giulia Vezzani, John Schulman, Emanuel Todorov, and Sergey Levine.
The environment is based on the Adroit manipulation platform, a 28 degree of freedom system which consists of a 24 degrees of freedom ShadowHand and a 4 degree of freedom arm. The task to be completed consists on picking up a hammer with and drive a nail into a board. The nail position is randomized and has dry friction capable of absorbing up to 15N force. Task is successful when the entire length of the nail is inside the board.
Action Space¶
The action space is a Box(-1.0, 1.0, (26,), float32). The control actions are absolute angular positions of the Adroit hand joints. The input of the control actions is set to a range between -1 and 1 by scaling the real actuator angle ranges in radians.
The elements of the action array are the following:
Num |
Action |
Control Min |
Control Max |
Angle Min |
Angle Max |
Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Angular up and down movement of the full arm |
-1 |
1 |
-0.4 (rad) |
0.25 (rad) |
A_ARRx |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Angular left and right and down movement of the full arm |
-1 |
1 |
-0.3 (rad) |
0.3 (rad) |
A_ARRy |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint (radial/ulnar deviation) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.524 (rad) |
0.175 (rad) |
A_WRJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.79 (rad) |
0.61 (rad) |
A_WRJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.44 (rad) |
0.44(rad) |
A_FFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_FFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the forefinger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_FFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the forefinger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_FFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
8 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.44 (rad) |
0.44(rad) |
A_MFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
9 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_MFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
10 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the middle finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_MFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
11 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the middle finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_MFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.44 (rad) |
0.44(rad) |
A_RFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_RFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_RFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
15 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the ring finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_RFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
16 |
Angular position of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
0.7(rad) |
A_LFJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
17 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.44 (rad) |
0.44(rad) |
A_LFJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
18 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_LFJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
19 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the little finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_LFJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
20 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the little finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.6 (rad) |
A_LFJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
21 |
Horizontal angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-1 |
1 |
-1.047 (rad) |
1.047 (rad) |
A_THJ4 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
22 |
Vertical Angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-1 |
1 |
0 (rad) |
1.3 (rad) |
A_THJ3 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
23 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger (adduction/abduction) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.26 (rad) |
0.26(rad) |
A_THJ2 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
24 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-0.52 (rad) |
0.52 (rad) |
A_THJ1 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
25 |
Angular position of the IP joint of the thumb finger (flexion/extension) |
-1 |
1 |
-1.571 (rad) |
0 (rad) |
A_THJ0 |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
Observation Space¶
The observation space is of the type Box(-inf, inf, (46,), float64). It contains information about the angular position of the finger joints, the pose of the palm of the hand, the pose of the hammer and nail, and external forces on the nail.
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Joint Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Site Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint Type |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Angular position of the vertical arm joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
ARRx |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Angular position of the horizontal arm joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
ARRy |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Angular position of the horizontal wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
WRJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Angular position of the vertical wrist joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
WRJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
FFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the forefinge |
-Inf |
Inf |
FFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
FFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the forefinger |
-Inf |
Inf |
FFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
8 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
MFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
9 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
MFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
10 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
MFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
11 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the middle finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
MFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
12 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
RFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
13 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
RFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
14 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
RFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
15 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the ring finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
RFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
16 |
Angular position of the CMC joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
LFJ4 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
17 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
LFJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
18 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
LFJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
19 |
Angular position of the PIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
LFJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
20 |
Angular position of the DIP joint of the little finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
LFJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
21 |
Horizontal angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
THJ4 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
22 |
Vertical Angular position of the CMC joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
THJ3 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
23 |
Horizontal angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
THJ2 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
24 |
Vertical angular position of the MCP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
THJ1 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
25 |
Angular position of the IP joint of the thumb finger |
-Inf |
Inf |
THJ0 |
- |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
26 |
Insertion displacement of nail |
-Inf |
Inf |
nail_dir |
- |
slide |
position (m) |
27 |
Linear velocity of the hammer in the x direction |
-1 |
1 |
OBJTx |
- |
free |
velocity (m/s) |
28 |
Linear velocity of the hammer in the y direction |
-1 |
1 |
OBJTy |
- |
free |
velocity (m/s) |
29 |
Linear velocity of the hammer in the z direction |
-1 |
1 |
OBJTz |
- |
free |
velocity (m/s) |
30 |
Angular velocity of the hammer around x axis |
-1 |
1 |
OBJRx |
- |
free |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
31 |
Angular velocity of the hammer around y axis |
-1 |
1 |
OBJRy |
- |
free |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
32 |
Angular velocity of the hammer around z axis |
-1 |
1 |
OBJRz |
- |
free |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
33 |
Position of the center of the palm in the x direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
S_grasp |
- |
position (m) |
34 |
Position of the center of the palm in the y direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
S_grasp |
- |
position (m) |
35 |
Position of the center of the palm in the z direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
S_grasp |
- |
position (m) |
36 |
Position of the hammer’s center of mass in the x direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
Object |
- |
position (m) |
37 |
Position of the hammer’s center of mass in the y direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
Object |
- |
position (m) |
38 |
Position of the hammer’s center of mass in the z direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
Object |
- |
position (m) |
39 |
Relative rotation of the hammer’s center of mass with respect to the x axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
Object |
- |
angle (rad) |
40 |
Relative rotation of the hammer’s center of mass with respect to the y axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
Object |
- |
angle (rad) |
41 |
Relative rotation of the hammer’s center of mass with respect to the z axis |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
Object |
- |
angle (rad) |
42 |
Position of the nail in the x direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
S_target |
- |
position (m) |
43 |
Position of the nail in the y direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
S_target |
- |
position (m) |
44 |
Position of the nail in the z direction |
-Inf |
Inf |
- |
S_target |
- |
position (m) |
45 |
Linear force exerted on the head of the nail |
-1 |
1 |
- |
S_target |
- |
Newton (N) |
Rewards¶
The environment can be initialized in either a dense or sparse reward variant.
In the dense reward setting, the environment returns a dense reward function that consists of the following parts:
get_to_hammer: increasing negative reward the further away the palm of the hand is from the hammer. This is computed as the 3 dimensional Euclidean distance between both body frames. This penalty is scaled by a factor of0.1in the final reward.take_hammer_head_to_nail: increasing negative reward the further away the head of the hammer if from the head of the nail. This reward is also computed as the 3 dimensional Euclidean distance between both body framesmake_nail_go_inside: negative cost equal to the 3 dimensional Euclidean distance from the head of the nail to the board. This penalty is scaled by a factor of10in the final reward.velocity_penalty: Minor velocity penalty for the full dynamics of the environments. Used to bound the velocity of the bodies in the environment. It equals the norm of all the joint velocities. This penalty is scaled by a factor of0.01in the final reward.lift_hammer: adds a positive reward of2if the hammer is lifted a greater distance than0.04meters in the z direction.hammer_nail: adds a positive reward the closer the head of the nail is to the board.25if the distance is less than0.02meters and75if it is less than0.01meters.
The sparse reward variant of the environment can be initialized by calling gym.make('AdroitHandHammerSparse-v1').
In this variant, the environment returns a reward of 10 for environment success and -0.1 otherwise.
Starting State¶
To add stochasticity to the environment the z position of the board with the nail is randomly initialized each time the environment is reset. This height is sampled from
a uninform distribution with range [0.1,0.25].
The joint values of the environment are deterministically initialized to a zero.
For reproducibility, the starting state of the environment can also be set when calling env.reset() by passing the options dictionary argument (https://gymnasium.farama.org/api/env/#gymnasium.Env.reset)
with the initial_state_dict key. The initial_state_dict key must be a dictionary with the following items:
qpos: np.ndarray with shape(33,), MuJoCo simulation joint positionsqvel: np.ndarray with shape(33,), MuJoCo simulation joint velocitiesboard_pos: np.ndarray with shape(3,), cartesian coordinates of the board with the nail
The state of the simulation can also be set at any step with the env.set_env_state(initial_state_dict) method.
Episode End¶
The episode will be truncated when the duration reaches a total of max_episode_steps which by default is set to 200 timesteps.
The episode is never terminated since the task is continuing with infinite horizon.
Arguments¶
To increase/decrease the maximum number of timesteps before the episode is truncated the max_episode_steps argument can be set at initialization. The default value is 50. For example, to increase the total number of timesteps to 400 make the environment as follows:
import gymnasium as gym
import gymnasium_robotics
gym.register_envs(gymnasium_robotics)
env = gym.make('AdroitHandHammer-v1', max_episode_steps=400)
Version History¶
v1: refactor version of the D4RL environment, also create dependency on newest mujoco python bindings maintained by the MuJoCo team in Deepmind.
v0: legacy versions in the D4RL.